Lab 9
An Overview of Basic
Programming
CS211 Lab Policy:
- This lab exercise will not be graded.
- Submit as much as you have completed before the end of the lab period in
which it is assigned.
- If you do not finish this lab work, it is to your advantage to finish it
outside of class. Please re-submit your finished work to the course web
site.
- You may receive help from anyone in completing this lab.
- You may not submit another student's code as part of your
lab.
Instructions:
You will create two MATLAB program files named
lab9a.m and
lab9b.m for this lab. The function lab9a() should calculate and
display a "cellular automata" by implementing code for each step described below.
Then you should create a more "readable" version of this code and store it in
function lab9b().
Problem Steps for lab9a:
- Begin your program by clearing the command window and displaying your
name and "Lab 9".
- Set two constants values: Blue = 1; Red = 64;
- Create a 2D array that is 300x300 where all
elements are equal to Blue.
- Set the single element on the 1st row and the middle column of your array to
Red.
- For every element in your 2D array from the 2nd row to the last row, and
from the 2nd column to the next-to-last column, if an element has the
following relationship to its "neighbors", set its value to
Red.
if the neighbor that is on the previous row and one column
back is Red, or
if the neighbor that is on the previous row and one column
over is Red,
but not if both diagonal neighbors are Red
-
Display the "cellular automata" you just created by using
the MATLAB image() function. (Your
output should look something like the figure below.)
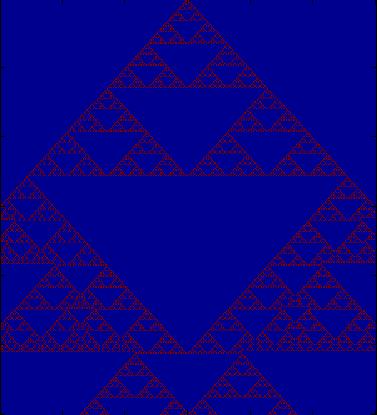
- When your program is working correctly, make sure it is saved to the
file lab9a.m. Then make a copy of
this file called lab9b.m
(And change the function name to
lab9b.)
Creating more "readable" code:
Modify your code in the file
lab9b.m to make
it more "readable" by performing the tasks below. If you are confused
about a particular task, refer
to the lesson notes and the sample solution
from a previous
semester's PEX 1 assignment
to understand what "readable" code is.
- Create constants for the image size (both rows and columns) at the top
of your program and change every occurrence of the value 300 (or 299) to the
appropriate constant name. Make sure that the "middle column" is always half
the total number of columns.
- Make sure all your code is indented properly (use CTRL-I).
- Add appropriate comments and a program comment header block.
- Group related statements into code blocks separated by one blank
line.
- Modify any variable names that are not descriptive.
Please spend any remaining lab time working on PEX1.
Turn-in:
Submit your
lab9a.m and
lab9b.m files.
References: A New Kind of Science, by Stephen Wolfram, Wolfram
Media, Inc, ISBN 1-57955-008-8.